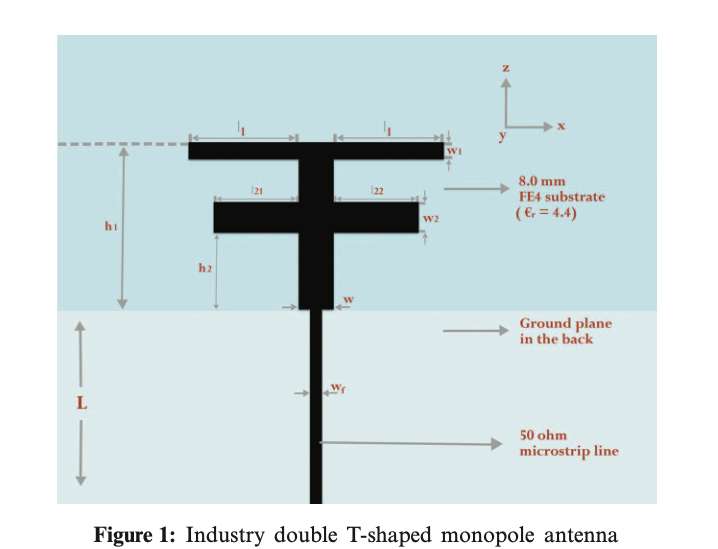
Advance Artificial Intelligence Technique for Designing Double T-Shaped Monopole Antenna
Machine learning (ML) has taken the world by a tornado with its prevalent applications in automating ordinary tasks and using turbulent insights throughout scientific research and design strolls.ML is a massive area within artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on obtaining valuable information out of data, explaining why ML has often been related to stats and data science. An advanced meta-heuristic optimization algorithm is proposed in this work for the optimization problem of antenna architecture design. The algorithm is designed, depending on the hybrid between the Sine Cosine Algorithm
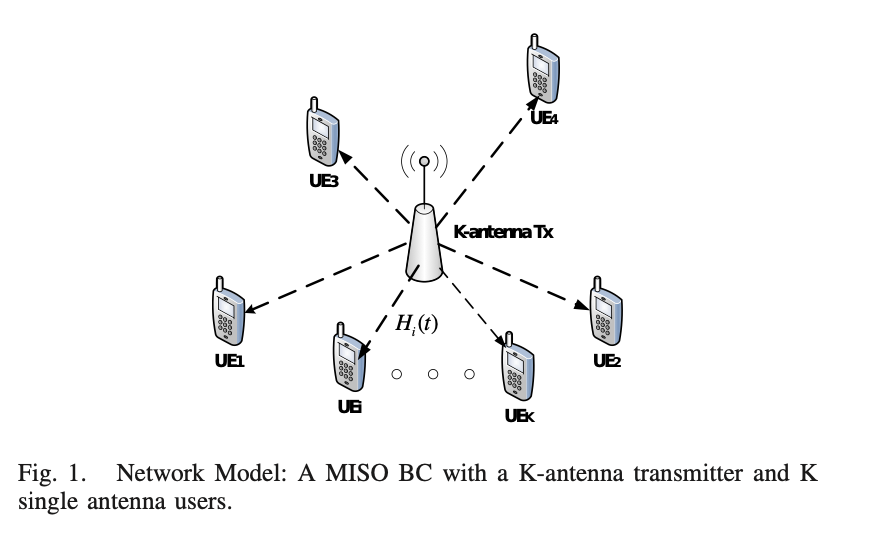
Achievable degrees of freedom of the K-user MISO broadcast Channel with alternating CSIT via interference creation-resurrection
Channel state information at the transmitter affects the degrees of freedom of the wireless networks. In this paper, we analyze the DoF for the K-user multiple-input single-output (MISO) broadcast channel (BC) with synergistic alternating channel state information at the transmitter (CSIT). Specifically, the CSIT of each user alternates between three states, namely, perfect CSIT (P), delayed CSIT (D) and no CSIT (N) among different time slots. For the K-user MISO BC, we show that the total achievable degrees of freedom (DoF) are given by K2/K2-1 through utilizing the synergistic benefits of
Space-time coding for an energy harvesting cooperative secondary terminal
In this letter, we consider a cognitive scenario where an energy harvesting secondary user (SU) shares the channel with a primary user (PU). The SU is equipped with two antennas. It maintains a finite capacity energy queue and two infinite capacity data queues: one for storing its own data packets and the other for storing the primary undelivered data packets. The PU communicates with its destination whenever it has data at its queue head. During idle sessions of the PU, if the secondary energy queue maintains at least κ packets, the SU employs the Alamouti coding scheme over two of its data
Effective area spectral efficiency for wireless communication networks with interference management
In this paper, we introduce a new metric, namely, effective area spectral efficiency (EASE), to quantify the spectral efficiency as well as the spatial properties of point-to-point transmission systems and decode and forward (DF) relaying communications networks with interference management. For each transmission mode, we derive a closed-form expression for the maximum transmission range under Rayleigh fading environment. Based on the maximum transmission range, we define and derive the average affected area and the average ergodic capacity. We then introduce the EASE expression to quantify
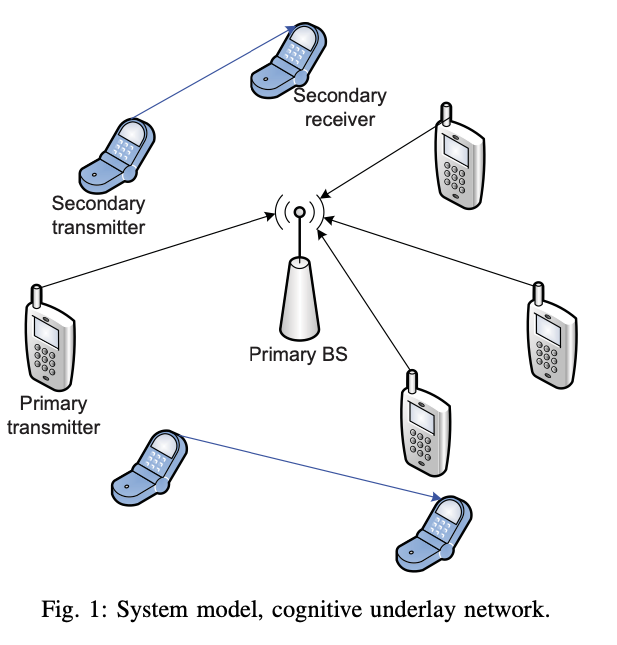
Admission and power control for spectrum sharing cognitive radio networks
We investigate the problem of admission and power control considering a scenario where licensed, or primary, users and cognitive radios, or secondary users, are transmitting concurrently over the same band. The primary users share a common receiver and the interference on this receiver from secondary users should be strictly limited to a certain level. Each secondary link is assumed to have a minimum quality of service (QoS) requirement that should be satisfied together with the interference limit constraint, otherwise the secondary link is not admitted. Under those constraints, admission and
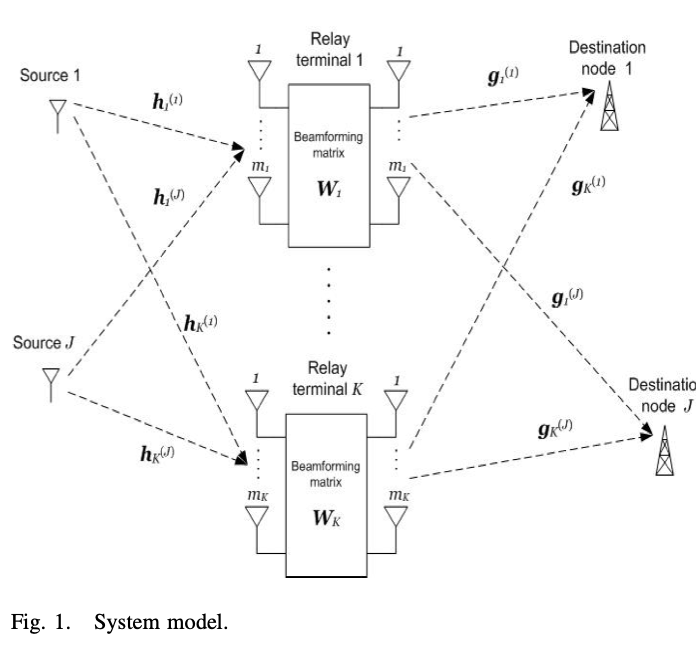
Adaptive linearly constrained minimum variance beamforming for multiuser cooperative relaying using the kalman filter
In this paper, we consider a wireless communication scenario with multiple source-destination pairs communicating through several cooperative amplify-and-forward relay terminals. The relays are equipped with multiple antennas that receive the source signals and transmit them to the destination nodes. We develop two iterative relay beamforming algorithms that can be applied in real-time. In both algorithms, the relay beamforming matrices are jointly designed by minimizing the received power at all the destination nodes while preserving the desired signal at each destination. The first algorithm
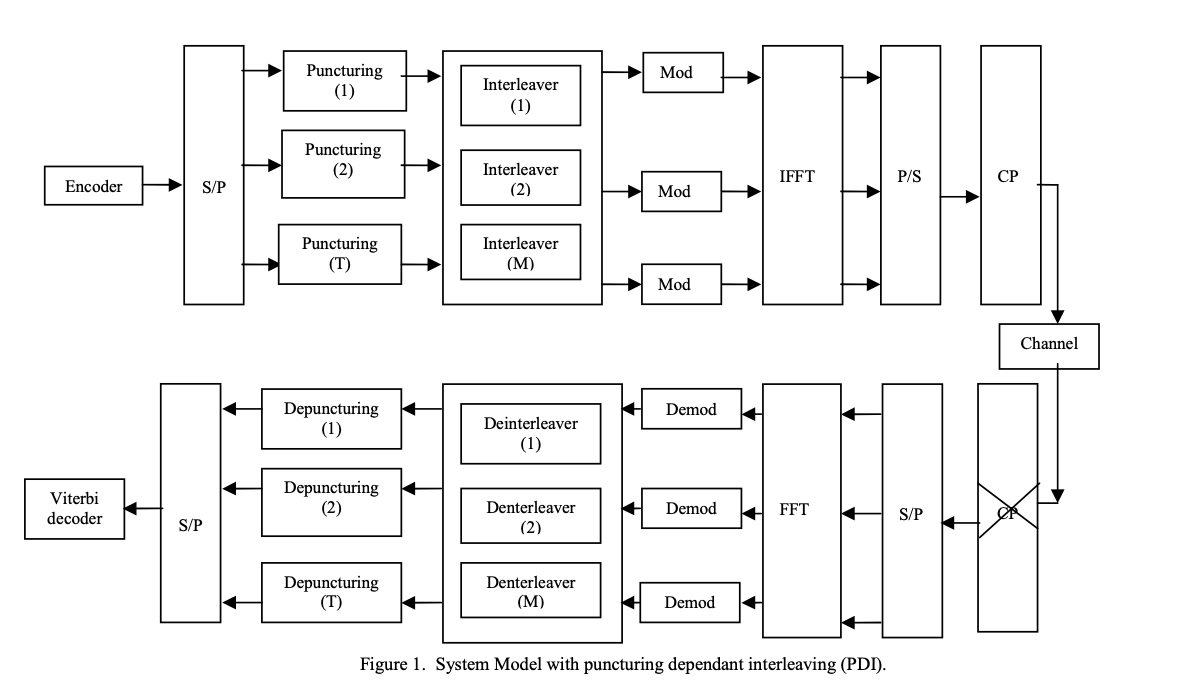
Adaptive puncturing for coded OFDMA systems
A scheme is proposed for adaptively changing the code rate of coded OFDMA systems via changing the puncturing rate within a single codeword (SCW). In the proposed structure, the data is encoded with the lowest available code rate then it is divided among different resource blocks (tiles) where it is punctured adaptively based on some measure of the channel quality for each tile. The proposed scheme is compared against using multiple codewords (MCWs) where the transmitter divides the data over tiles and encodes them separately. We investigate two different adaptive modulation and coding (AMC)
On the delay limited secrecy capacity of fading channels
In this paper, the delay limited secrecy capacity of the flat fading channel is investigated under two different assumptions on the available transmitter channel state information (CSI). The first scenario assumes perfect prior knowledge of both the main and eavesdropper channel gains. Here, upper and lower bounds on the secure delay limited capacity are derived and shown to be tight in the high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regime (for a wide class of channel distributions). In the second scenario, only the main channel CSI is assumed to be available at the transmitter. Remarkably, under this
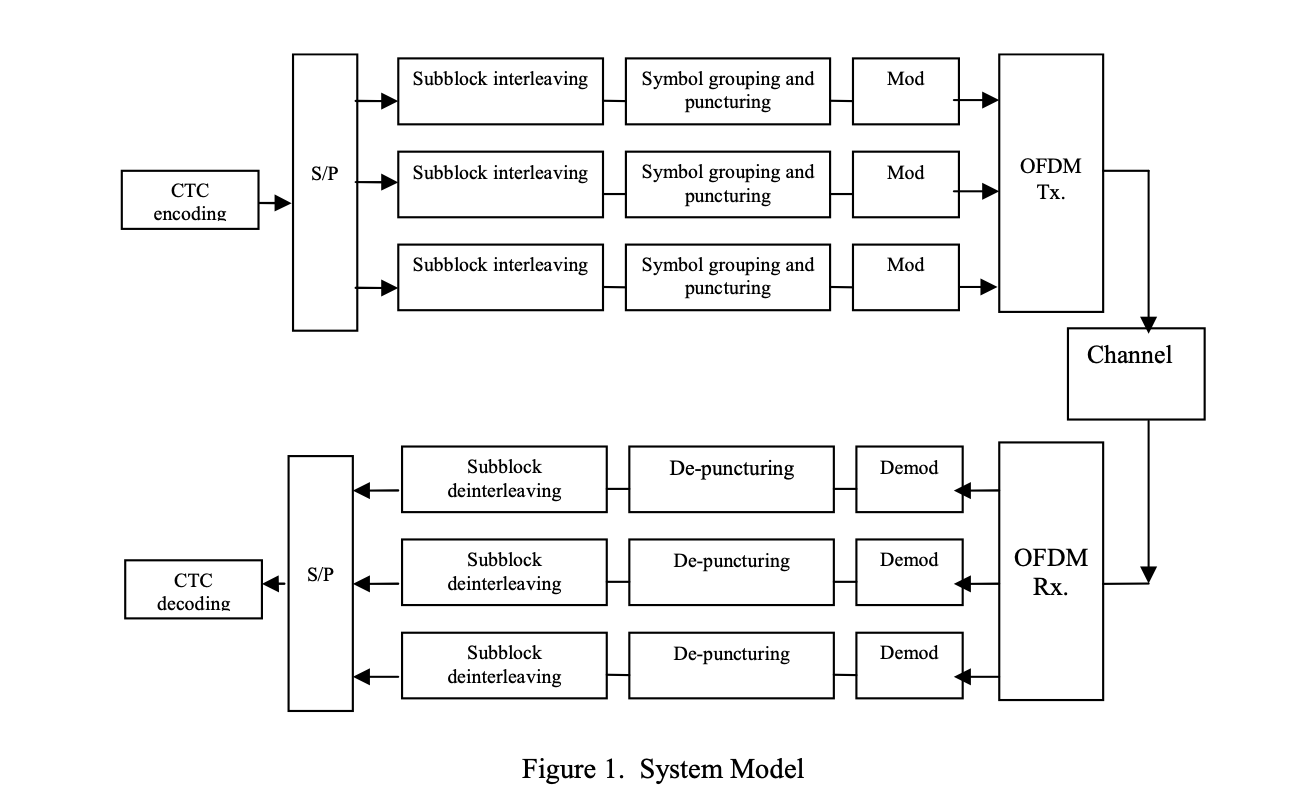
Adaptive puncturing and rate selection in single-codeword turbo-coded OFDMA
This paper proposes using adaptive puncturing for rate-adaptive OFDMA systems utilizing turbo codes. The scheme is based on adaptively puncturing a Single Code Word (SCW) and hence adaptively changing the rate within the codeword. We compare the SCW against the Multiple Code-Words (MCWs) scheme where different rates are obtained by separate encoding, puncturing, and interleaving on a per-tile basis. Noticeable gains are obtained over the MCW scheme due to the use of larger turbo block sizes and hence larger interleavers. The SCW has around 1dB gain in goodput compared to MCWs, with much
HyberLoc: Providing physical layer location privacy in hybrid sensor networks
In many hybrid wireless sensor networks' applications, sensor nodes are deployed in hostile environments where trusted and un-trusted nodes co-exist. In anchor-based hybrid networks, it becomes important to allow trusted nodes to gain full access to the location information transmitted in beacon frames while, at the same time, prevent un-trusted nodes from using this information. The main challenge is that un-trusted nodes can measure the physical signal transmitted from anchor nodes, even if these nodes encrypt their transmission. Using the measured signal strength, un-trusted nodes can still
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 40
- Next page ››
